Scotland, UK Overview
Scotland is the most northern of the United Kingdom’s four constituent nations, involving about 33% of the island. In the fifth century CE, Irish Celts chose the west shoreline of England, naming it “Scotland.” Scotland’s name comes from the Latin Scotia, signifying “place that is known for the Scots.” Caledonia is a term habitually used to allude to Scotland, especially in verse. Caledonii was the Roman name for a clan that lived in what is presently northwest Scotland.
Scotland’s brutal environment and outrageous weather patterns have made it hard for some ages to live there, however they have appreciated it for its normal excellence and extraordinary culture. During the Scottish Illumination, scholars like Francis Hutcheson and Adam Smith manufactured significant commitments to political and down to earth hypotheses of progress. Scottish creators, designers, and money managers like Alexander Graham Chime, James Watt, Andrew Carnegie, and John McAdam helped Scotland’s impact a long ways past its boundaries.
Scotland-Britain relations have been stressed since the two nations joined in 1707 to frame the Unified Realm of Extraordinary England. Regardless of weighty English impact, Scotland has long kept up with its autonomy, sticking to authentic reality and legend to safeguard public personality and the Scots lingo of English.

Scotland's Flag | |
Capital | Edinburgh |
Status | Constituent countrie |
National Language | English |
Religion | 53.8% Christian, 36.7% no religion, 2.6% other |
ISO 3166 code | GB-SCT |
Area | 77,933 km2 (30,090 sq mi) |
Population | 5,313,600 |
Timezone | Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
Summer Timezone | British Summer Time (UTC+1) |
Currency | Pound sterling (GBP; £) |
GDP | £145.245 billion |
Geological Depiction of Scotland
The Aegean, Atlantic, North, and English Channels line Scotland’s southern, western, and northern boundaries, as well as its eastern boundary. The west coast is dabbed with enormous islands going in size from little shakes to the huge Lewis and Harris, Skye, and Reflect on expanses of land (ocean lochs or fjords). Orkney and Shetland islands are found north of Scotland. 274 miles (441 kilometers) from Cape Rage to the Reflect of Galloway, and 154 miles wide from Applecross in the western Good countries to Buchan Ness in the eastern Grampians. Scotland’s central area has two parts: north and south (248 km). With just 30 miles of land isolating the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forward, Scotland’s two significant estuarine channels on its west and east drifts, from the ocean, by far most of spots are inside 40 to 50 miles (65 to 80 kilometers) of the ocean.
The Good countries are in the north, the Midland Valley (Focal Marshes) is in the center, and the Southern Uplands are in the south. (The last two are essential for the Marshes social locale, which incorporates the previous two.) Low-lying regions run the length of the Midland Valley and the US east coast. The east coast’s smoother frame stands out from the west coast’s rough diagram, bringing about a geological as well as a north-south separation. The Glen Mor (Glen Albyn) separation point isolates the High countries from the remainder of the country. Toward the north of Glen Mor is an old level dissolved into a progression of pinnacles of comparative level isolated by glens cut by glacial masses (valleys). The Lewisian Complex rocks have been worn out by serious glaciation to shape a hummocky scene interspersed by little lochs and jutting rocks from meager, acidic soil. The eminent Torridonian sandstone mountains have endured into sheer precipices, rock patios, and zeniths.
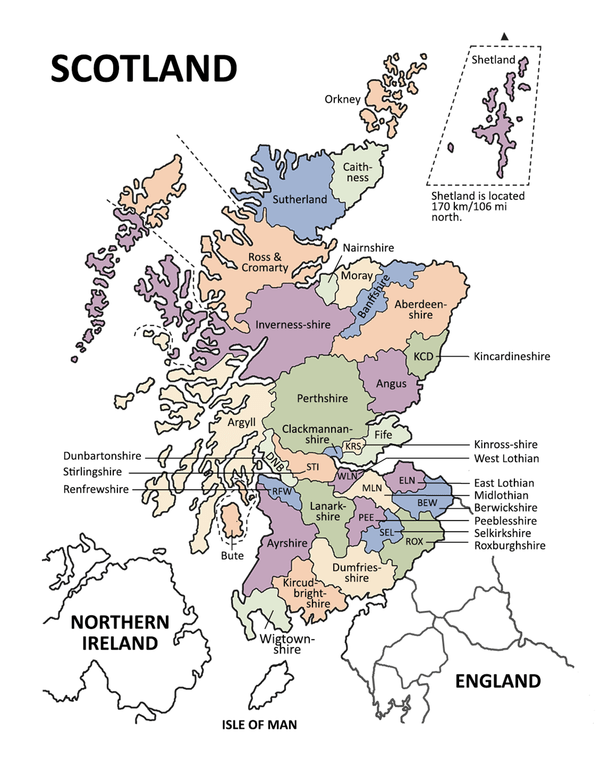
The Grampian Mountains are found southeast of Glen Mor, however there are interruptions, for example, the Cairngorm Mountains’ granitic masses. The Grampians are less rough and tough than the Northwest Mountains, being more adjusted and lush, with bigger level regions. The region has a portion of England’s most elevated mountains, including Ben Nevis (4,406 feet), which has bluffs and zeniths that make getting over troublesome (1,343 meters). Rannoch Field, a ruined spread of swamps and granitic rocks interspersed by tight, profound lochs like Rannoch and Ericht, is the most striking model (Rannoch Field is the most striking of these). The Good country Limit Issue runs upper east southwest from Stonehaven, only south of Aberdeen, to Helensburgh on the Waterway Clyde, going through Loch Lomond, Scotland’s biggest freshwater body. The southern limit of the Midland Valley is partitioned by a shortcoming that runs from upper east to southwest, starting with the Lammermuir and Moorfoot slopes. It’s deceptive to call this piece of Scotland the Swamps in light of the fact that, while it’s low contrasted with different pieces of Scotland, it’s not level. Volcanic slopes like the Sidlaws, Ochils, Campsies, and Pentlands overwhelm the scene (579 meters). The Southern Uplands are not quite as high as the High countries. Glaciation has made thin, level valleys that gap folding mountains into segments. The delicately inclining, lush, and adjusted slopes only east of Nithsdale open up into prolific Merse cultivating area toward the south. With time, the scene west of Nithsdale turns out to be more rough, with granitic interruptions around Loch Doon, and the dirt turns out to be more peaty and wet. Merrick’s high moorlands and slopes can uphold a sheep ranch at 2,766 feet (843 meters) above ocean level. The uplands slant down to the Solway Firth’s seaside fields in the south and the machair and Ponder of Galloway in the west.
The Economy of Scotland
Because of the issues that tormented numerous European nations during the 1970s and 1980s, including the far and wide disappointment of weighty ventures, Scotland’s economy endured extraordinarily during this period. Joblessness turned into a critical issue, especially in regions where significant businesses were in decline simultaneously. Different measures were executed by progressive states to advance the circumstance. As a result of the extraction of North Ocean oil and petroleum gas, as well as the improvement of high-innovation enterprises and other monetary areas, Scotland’s economy started to flourish during the 1980s.
Scotland’s economy stays little however open, representing around 5% of the complete commodity income of the Unified Realm. Beside London and the eastern locales of Britain, no other district in the Unified Realm has a higher total national output (Gross domestic product) per capita than the West Midlands, and its joblessness rate is moderately low. Undoubtedly, abundance dissemination in Scotland isn’t uniformly appropriated, and the typical joblessness rate disguises pockets of essentially higher joblessness in unambiguous areas and regions. Scottish financial turn of events, schooling, and preparing are all directed by the Scottish Parliament, in spite of the way that the English government has command over macroeconomic strategy in the country. This incorporates focal government spending, financing costs, and money related strategy in Scotland.
WHEN WERE THE ZIP (PIN) CODES INTRODUCED IN SCOTLAND?
Scotland Postal codes are regulated by the Universal Postal Union as well as Global Postal Codes. Postal codes in Scotland help confirm the location when transferring mail, and postal items or are used to fill in information when users register online with a request to enter a postal code or postal code.
In 1983, the U.S. Postal Service introduced an expanded Scotland ZIP code system that it called ZIP+4, often called “plus-four codes”, “add-on codes”, or “add ons”.
WHY ARE PIN CODES (ZIP CODES) SO IMPORTANT?
Postal codes (ZIP codes) are not something Scotland often use. But postal codes are one of the most important parts to use when you are sending or receiving couriers. The postal codes help the mailmen to speed up the sorting and delivery process for your courier to the right address. For example, in a large city like Edinburgh, there might be a street with similar or identical names, and in those cases, without correct postal codes (ZIP codes) delivering a parcel could be difficult.
These days postal codes have become well-known or subject of curiosity among youths because of the increasing adoption of technology and growth in online shopping habits.
How do you use Postal Codes (ZIP Code) for Vietnam while online shopping on eBay, Amazon, or other Platforms?
Search For Latest Scotland Postal Code and all region in Scotland
Scotland Postcode unit boundaries are created and maintained by the National Records of Scotland (NRS) for every live small user postcode so that the entire land surface of Scotland is covered by postcode polygons.
The dataset represents the smallest plotted unit in Scotland which supports the production of high quality statistics.
NRS publish these boundaries twice a year as part of the Scottish Postcode Directory (SPD) which should be considered the definitive source for postcode geographies in Scotland.
No. | Region in Scotlands | Postal Code |
01 | AB10, AB11, AB12, AB15, AB16, AB21, AB24, AB25 | |
02 | AB12, AB21, AB23, AB30, AB31, AB33, AB35, AB41,AB42, AB42, AB45, AB51, AB53, AB54..., | |
03 | DD2, DD3, DD4,....DD11, PH11, PH12 | |
04 | PA20, PA21,....PA77, G83, G84 | |
05 | EH1, EH10, EH11, EH12, EH13, EH14, EH15, EH16, EH17, EH2, EH3, EH4, EH5, EH6, EH7, EH8, EH9 | |
06 | FK10, FK11, FK12, FK13, FK14 | |
07 | DG1, DG2, DG3, ....DG14, DG15, DG16 | |
08 | DD1, DD2, DD3, DD4, DD5 | |
09 | KA1, KA2, KA3... KA16, KA17, KA18 | |
10 | G61, G62, G63, G64 | |
11 | EH21, EH22.... EH41, EH42 | |
12 | G46, G76, G77, G78 | |
13 | Eilean Siar | HS2, HS3, HS4, HS5, HS6, HS7, HS8, HS9 |
14 | Falkirk | FK1, FK2, FK3, FK4, FK5, FK6, FK7, EH49, EH51 |
15 | Fife | KY1, KY2, KY3... KY16, DD6, FK10 |
16 | Glasgow City | G1, G2, G11...G32, G33, G34, G40... G45, G46 . .... G51, G52, G53, G61, G62, ....G77, G78 |
17 | Highland | IV2, IV3... IV53, IV54, IV56.... KW1...KW14, PH20, PH21, PH39, PH41, PH49 |
18 | Inverclyde | PA11, PA13, PA14, PA15, PA16, PA18, PA19 |
19 | Midlothian | EH18, EH19, EH20, EH21, EH22, EH23, EH24, EH25, EH26, EH37 |
20 | Moray | AB37, AB38, AB54, AB55, AB56, IV30, IV31, IV32, IV36 |
21 | North Ayrshire | KA3, KA11, KA12, KA13, KA14, KA15, KA20, KA21, KA22, KA23, KA24, KA25, KA27, KA28, KA29, KA30, AND PA17 |
22 | North Lanarkshire | ML1, ML2, ML4, ML5, ML6, ML7, G65, G66, G67, G68, G69, FK4 |
23 | Orkney Islands | KW15, KW16, KW17 |
24 | Perth and Kinross | PH1, PH2.... PH10, PH11, PH13... PH17, PH18, KY3, KY13, PK14, PK15 |
25 | Renfrewshire | PA1, PA2, PA3...PA12, and G52 |
26 | Scottish Borders | TD1, TD2,..., TD14, TD15, ML12, EH26, EH45, EH46 |
27 | Shetland Islands | ZE1, ZE2, ZE3 |
28 | South Ayrshire | KA1, KA2, KA5....KA10, KA19, KA26 |
29 | South Lanarkshire | ML3, ML8, ML9, ML10, ML11, ML12, G71, G72, G74, G75, EH46 |
30 | Stirling | FK7, FK8, FK9, FK15, FK16, FK17, FK18, FK19, FK20, FK21, G62, G63 |
31 | West Dunbartonshire | G60, G81, G82, G83 |
32 | West Lothian | EH27, EH47, EH48, EH49, EH52, EH53, EH54, EH55 |


